Challenges and Initiatives in Recycling Printed Carrier Films
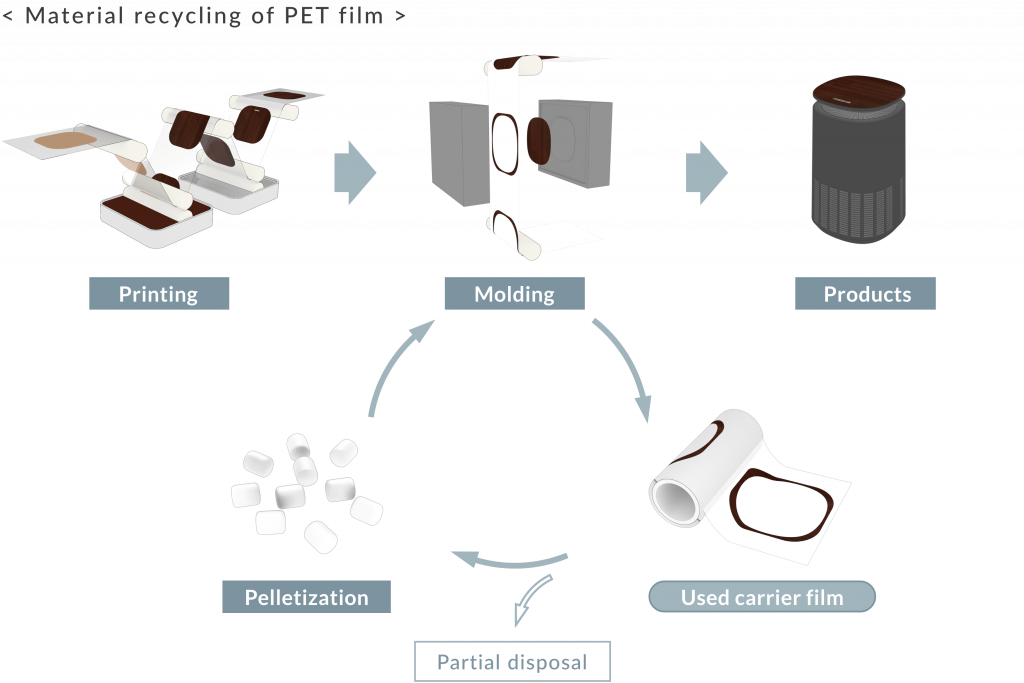
We have actively pursued the development of material recycling methods for printed carrier films and explored the potential of utilizing recycled resins. In the first phase of our material recycling initiatives, we employed 3D printing technology, and in the second phase, we used a small injection molding machine to mold recycled resins.
In this third phase, we are pleased to introduce our efforts to utilize recycled resins as the molding material for our specialty technology, In-Mold Decoration (IMD), which allows simultaneous molding and decoration.
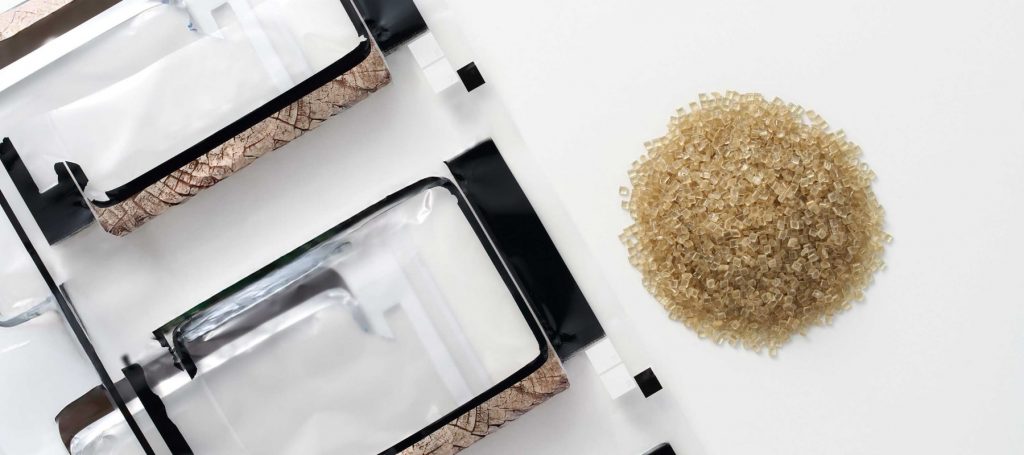
Carrier films, which are PET films used in the transfer molding process, are typically discarded after a single use. In our In-Mold Decoration (IMD) process, printed films are also disposed of after use. While we aim to recycle these materials, the presence of impurities, such as inks, makes direct recycling challenging.
In response, we conducted thorough testing to identify optimal conditions for pelletizing the recycled materials. Additionally, by adjusting molding parameters and developing a method for blending small amounts of other materials (dry blending), we successfully achieved a material recycling process compatible with our specialty, the IMD technique.


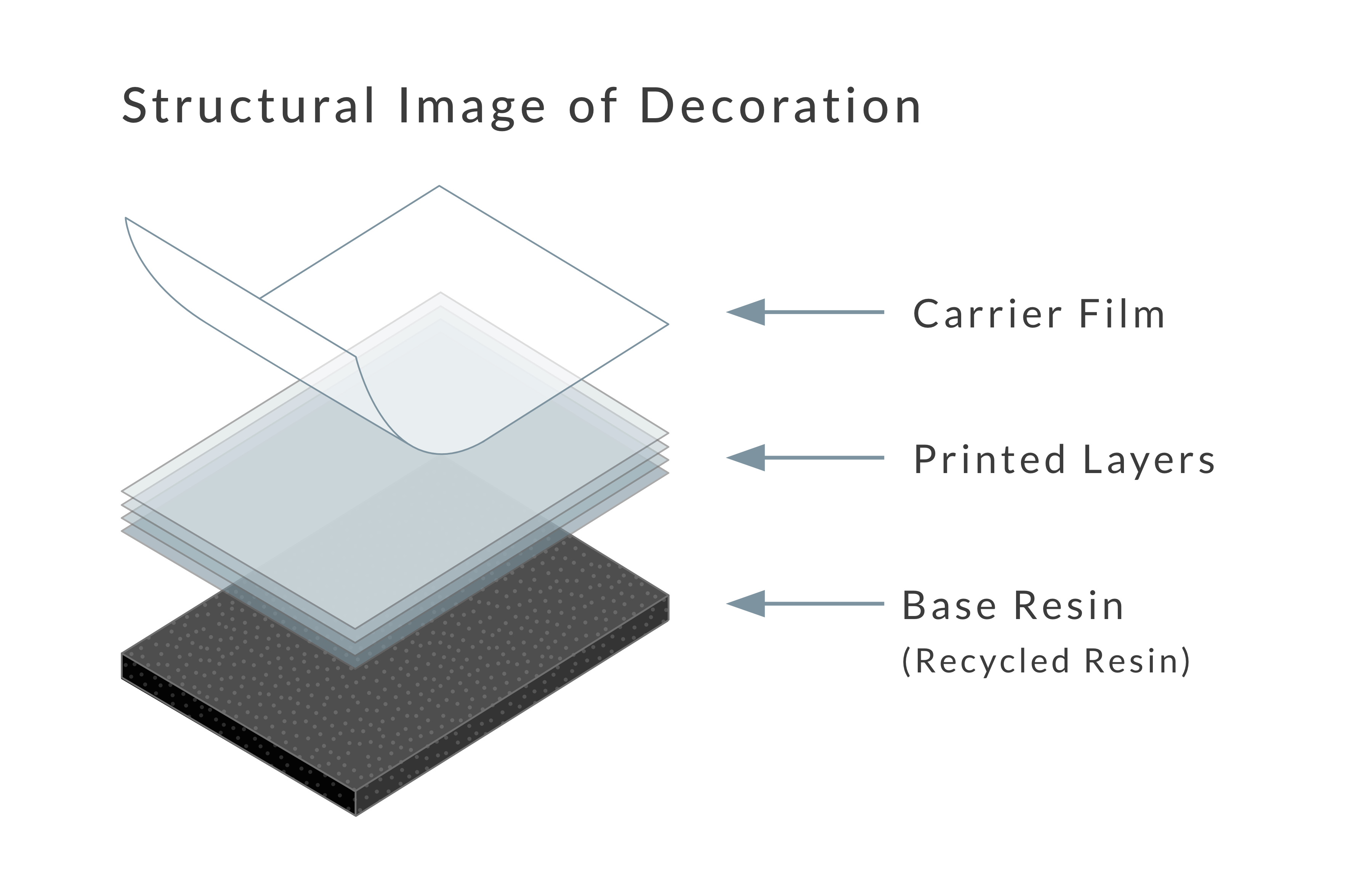
Carrier Film Recycling × IMD Surface Decoration Technology
Our IMD technology enables the injection molding of 3D-shaped plastics while simultaneously transferring designs printed on carrier films onto the surface of the molded product. A key advantage of this process is its ability to achieve a wide range of design expressions with decorative films while maintaining a simple workflow and offering high productivity through continuous molding. To ensure consistent quality, it is essential to consider the moldability of the base resin and its compatibility with the decorative film.
One of the primary challenges in using recycled PET resin for injection molding was achieving stable injection flow, due to the less-than-ideal flow properties of the resin. This issue was particularly pronounced at the nozzle tip, where clogging disrupted continuous molding, posing challenges for stable production.
To address this challenge, it became necessary to modify the characteristics of the recycled resin used in molding, leading us to explore blending it with other recycled materials. We focused on waste generated by a different in-house process. Unlike the IMD method, this process leaves printed film on the molded product, which then requires trimming during production, resulting in excess material. We experimented with pelletizing this waste to create recycled ABS pellets for reuse. As a result, we discovered that blending a small quantity of recycled ABS pellets with recycled PET pellets through drive blending significantly improved the stability of the injection molding.

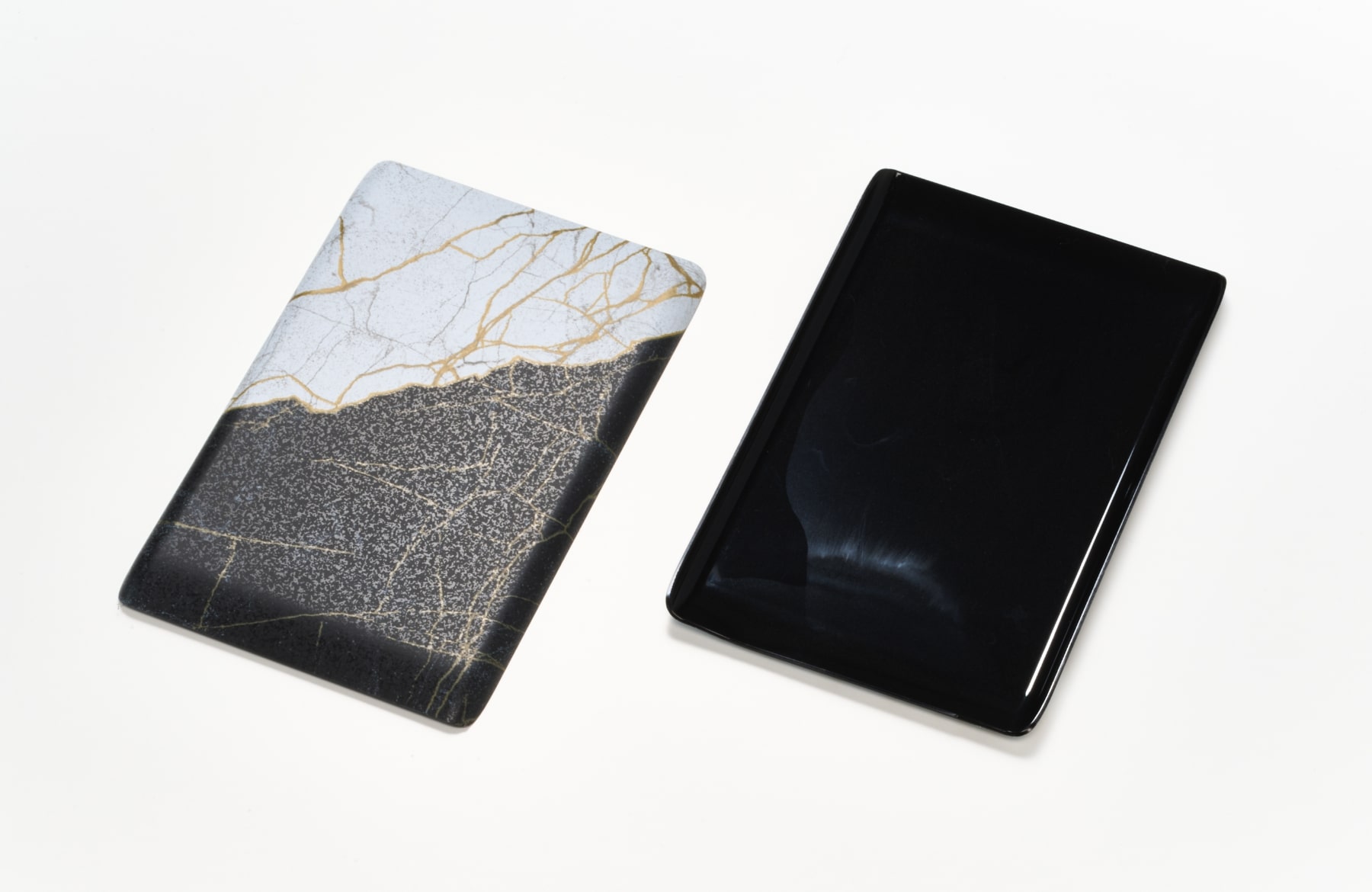
In this way, the blended recycled resin was made compatible with our IMD process using decorative films. Typically, molded products using recycled resin struggle to achieve the same level of uniformity as those made from virgin resin, particularly in appearance where inconsistencies and blemishes are more likely. However, by leveraging decorative films in this approach, we achieved refined surface designs, such as metallic and wood grain patterns. This effort goes beyond developing a technical recycling method – it represents a step toward expanding the potential of recycled materials by transforming them into high-value products that defy typical recycled standards.

Advancing a Sustainable Manufacturing Process
As the third phase in our efforts to recycle used carrier film, we introduced a new initiative that utilizes recycled resins as the molding material for our specialty IMD process. Through this approach, we have successfully pelletized carrier films used during the transfer process and incorporated them as molding resin, enabling efficient use of materials with minimal waste. This recycling of PET films – part of our ongoing efforts to reduce waste and promote material reuse in production – represents a key component of our commitment to sustainability.
Our company is dedicated to advancing environmental responsibility through multi-faceted approaches and will continue to prioritize sustainability in our processes.
The molded products created in this trial are featured in “CMF DESIGN 2024.”
Please note that the contents discussed in this article represent experimental efforts towards implementing material recycling.


