Blog
How to De-plasticize Trays Made by Vacuum Forming? Introducing Technologies to Achieve Reduced Environmental Impact
2024/04/05
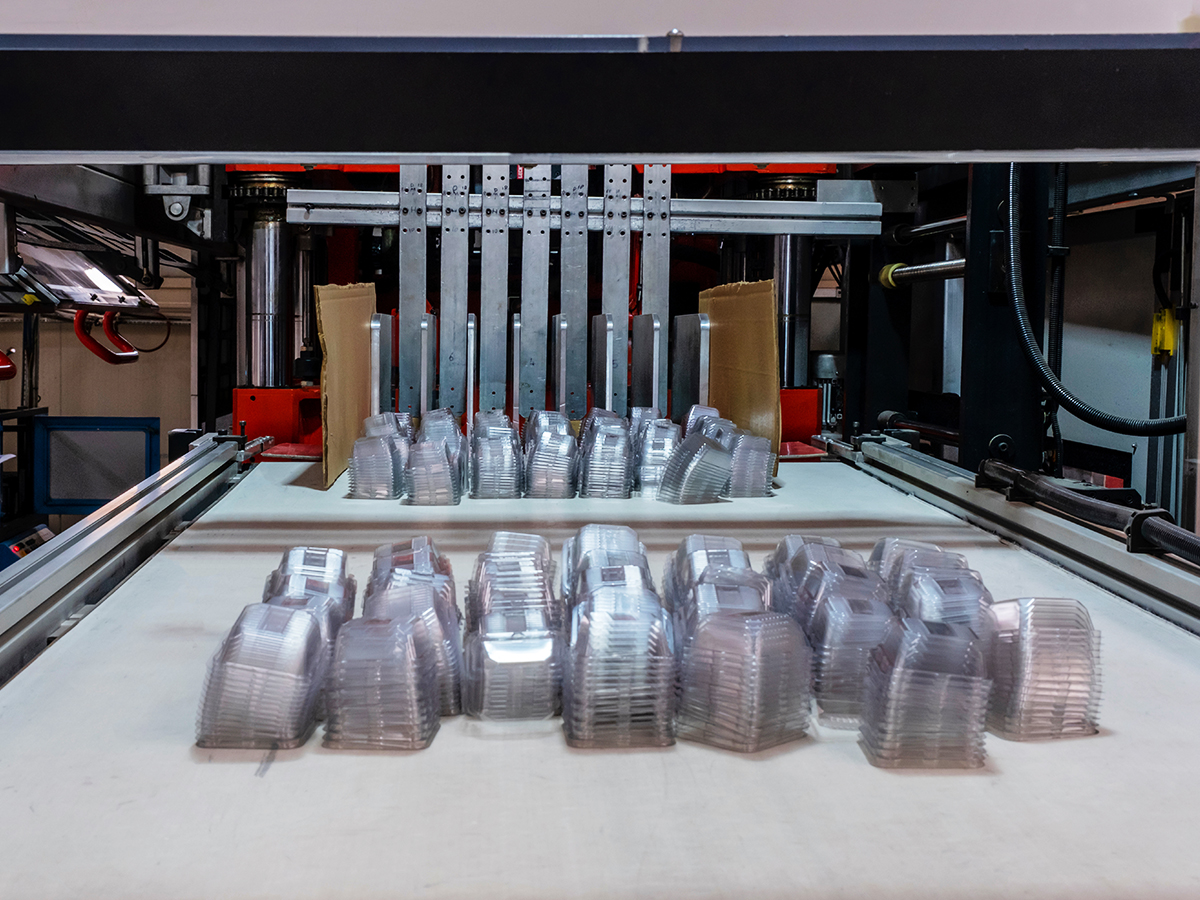

Vacuum-formed trays are one of the packaging materials that we commonly see in packages. They are essential for securing packaged products and preventing them from damage. However, because they are often discarded immediately after opening without being reused, vacuum-formed trays have become one of the challenges in the current trend of reducing plastic waste.
In this article, we will introduce various technologies to achieve de-plasticization of vacuum-formed trays, divided into two categories: technologies that have already been commercialized and new technologies.
Is it Difficult to De-plasticize Vacuum-formed Trays?
Vacuum forming is a technique of molding by heating and softening a plastic sheet, then forming it through suction. The materials for trays made by vacuum forming mainly include petroleum-based plastic materials such as polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), PET, and ABS.
The reason for using petroleum-based plastic materials is their good formability, high cushioning properties, and cost-effectiveness, which makes them suitable even for applications where they are discarded upon opening.

What is Required for De-plasticizing Vacuum-formed Trays?
To achieve de-plasticization, the following functionalities equivalent to current products are required:
- Product Protection
- The material must have cushioning and flexibility to prevent product damage.
- Formability
- The material must be able to reproduce various shapes excellently.
- Durability
- The material must withstand environmental changes during transport and the weight when loaded.
- Foreign Object Measures
- The material must be able to prevent the intrusion of dust and dirt. Also, sometimes anti-static functionality is required to prevent dust attraction due to static electricity.
- Low Outgassing
- The material should not produce gas that could potentially degrade the product after packaging.
Even Vacuum-formed Trays Can Be De-plasticized
As mentioned in the previous section, these functionalities are required for alternatives to vacuum-formed trays. Unfortunately, there are no environmentally friendly materials that meet all these features, which is why de-plasticization has not progressed much.
“ Recycled plastic ”, often seen as a material used for environmental measures, can basically be processed equivalently to virgin materials if they are the same plastic materials such as polypropylene (PP) and polystyrene (PS), and functionally, they are almost equivalent to conventional products. However, it is said that their functionality will decline with repeated use. Although it has a significant advantage in reducing the consumption of depleting resources, the use of new raw materials cannot be avoided in the long term.
In the next chapter, we will introduce the advantages and disadvantages of both already commercialized technologiesand new technologies to achieve de-plasticization of vacuum-formed trays.
Already Commercialized Technologies for De-plasticizing Vacuum-formed Trays
Technology for Assembling Paper (Cardboard)
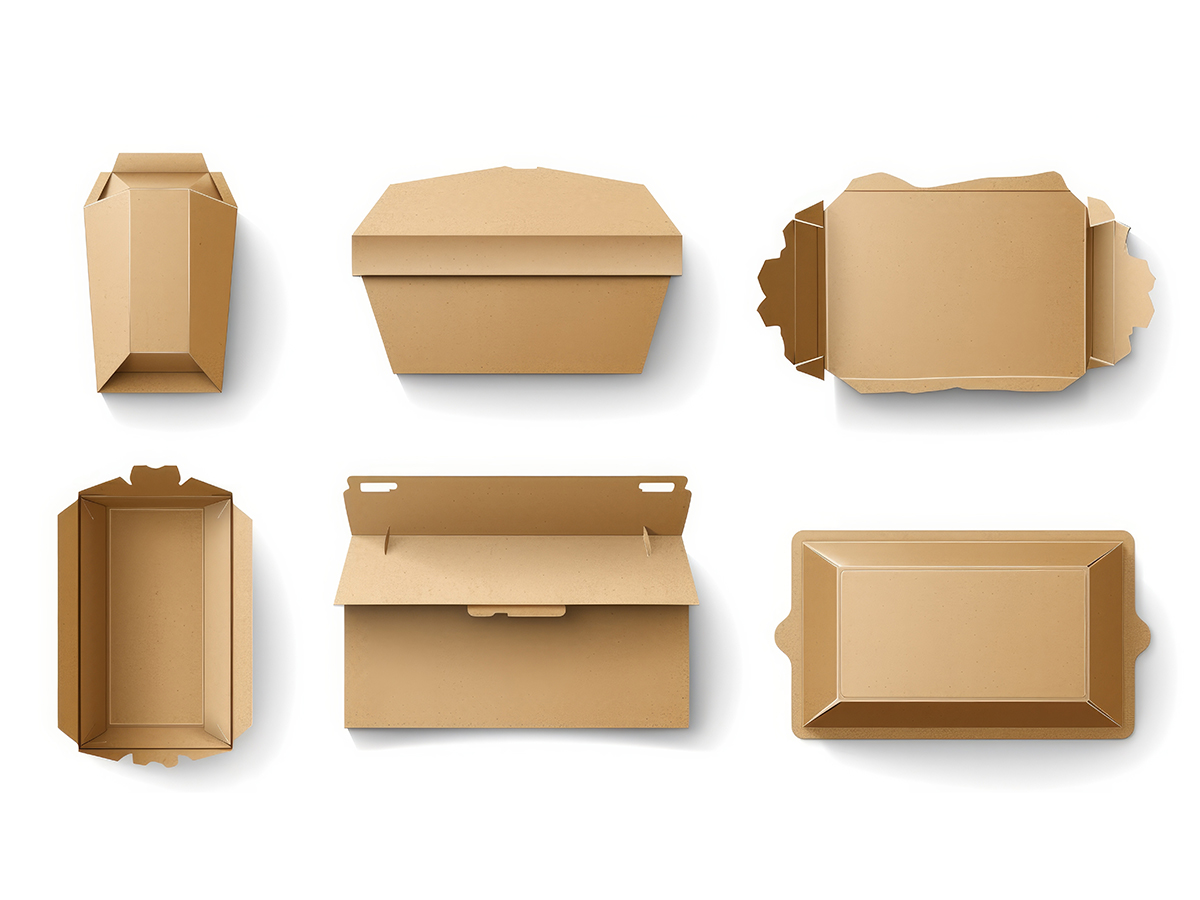

Cardboard is often used as a shipping box, but have you ever seen it used as a tray? By cleverly using cuts and creases, you can create various shapes, not just box-shaped. It used to be difficult to reproduce complex structures using cardboard, but with the use of 3D-CAD,complex designs have become possible, and trays made of paper materials like cardboard have become widespread.
The advantages of trays made of paper materials are that they can be manufactured at arelatively low cost and are easy to recycle. On the other hand, the need for manual labor and time in the process of bending and assembling cardboard can be considered as disadvantages. Also, it is difficult to reproduce curved surfaces and complex structures, and the shape reproducibility is still not as good as vacuum-formed trays.
Pulp Mold
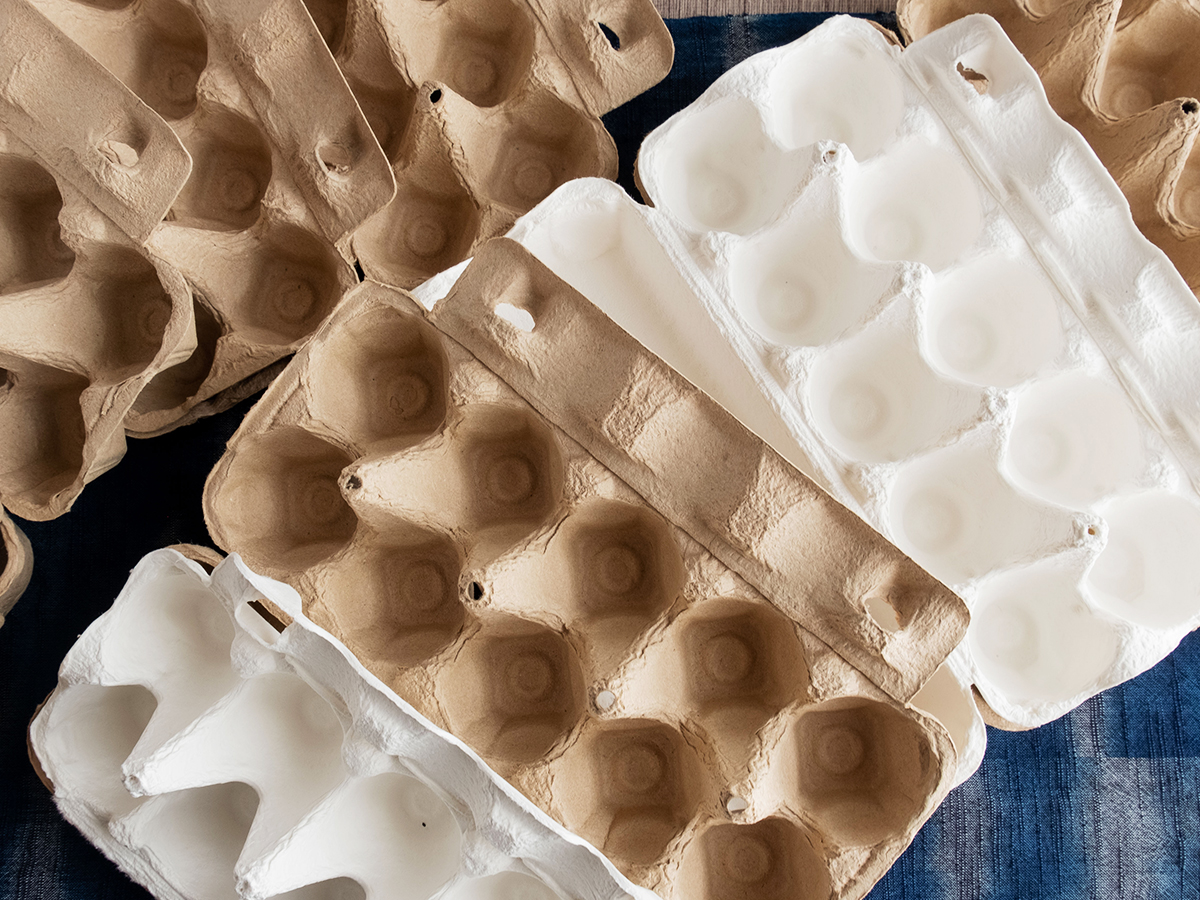

Pulp molding is a technique of depositing pulp, the raw material for paper, on a mold and drying it to form a shape. Since the material is pulp, just like paper, it does not use petroleum-based plastics. There are several types of pulp molds, which are explained in detail in the article titled “Molded Fiber– A Comprehensive Guide of Eco-Friendly and Their Innovative Applications”.
The advantage of pulp molding is that by using a mold to form it, the freedom of shape is much wider and the designability is higher compared to folding paper or cardboard.

On the other hand, like cardboard, it has the characteristic that pulp fibers can easily spill out when the cut surface or surface is rubbed, so it may not be suitable for products that require aesthetic appearance or delicate handling.
New Technologies Proposed by NISSHA to Achieve De-plasticization
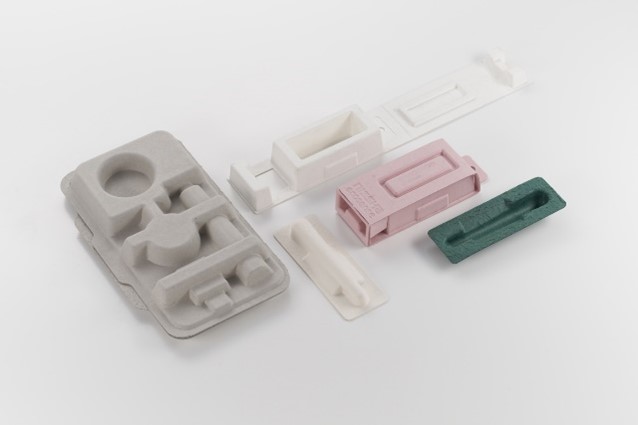
Pulp-Injection

Pulp-Injection is a technology that forms pellets, the main ingredients of which are pulp and starch, through injection molding. While achieving the same strength and thinness as plastic molded products, it can form trays with a paper-like texture.
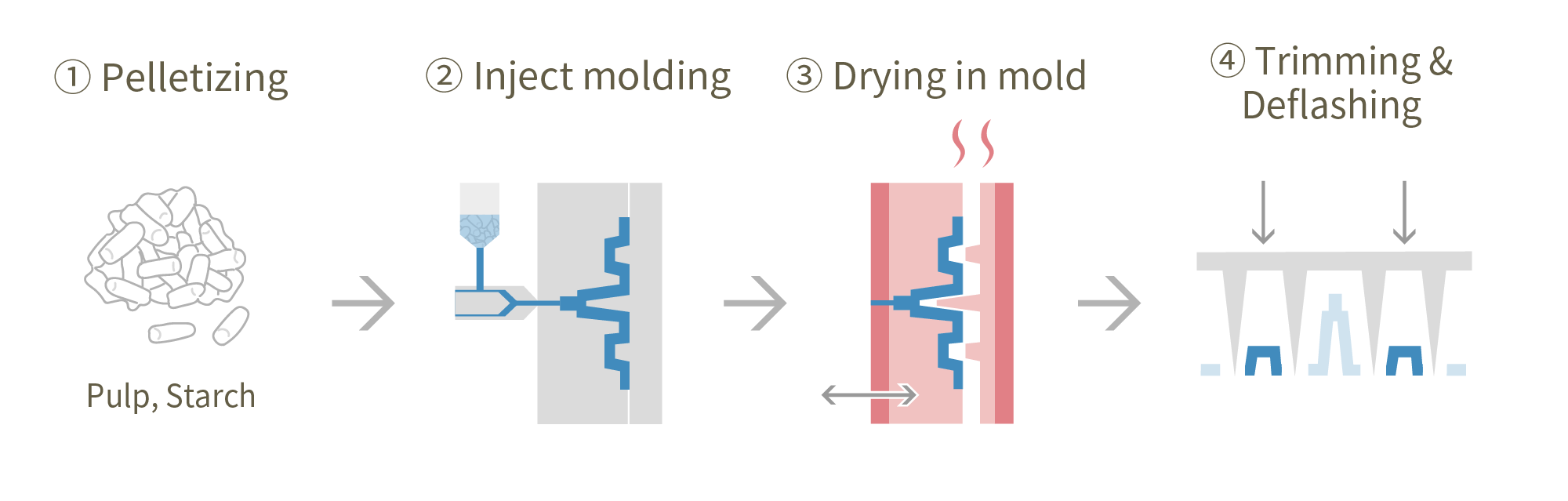
Because of its high shape freedom, it can reproduce three-dimensional shapes that cannot be achieved with paper or pulp molds. Therefore, by providing structures such as ribs, trays with higher protection can be created. Also, it is characterized by the less likely occurrence of dust caused by paper. Therefore, even for products that need to be put in individual plastic bags in pulp molding, they can be directly placed in Pulp-Injection trays.
PaperFoam®
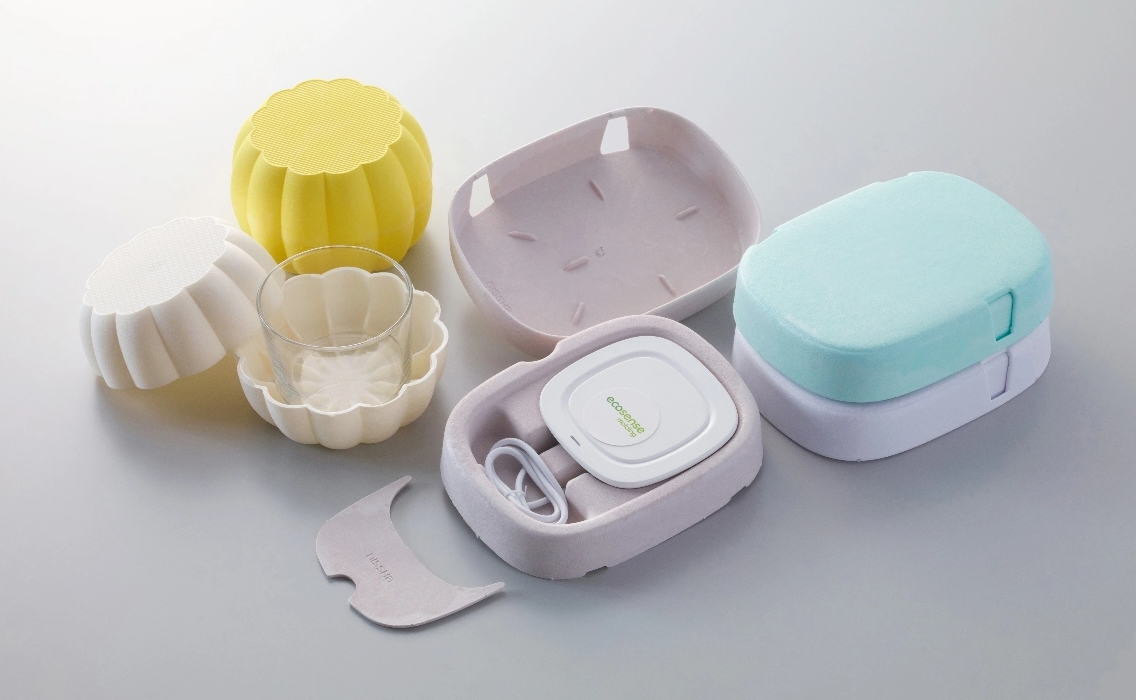

PaperFoam® is a technology that mixes the main ingredients (starch and pulp) with water, pours them into a special mold, and foams the material to form it. Therefore, it has hollows in the cross-section like Styrofoam.
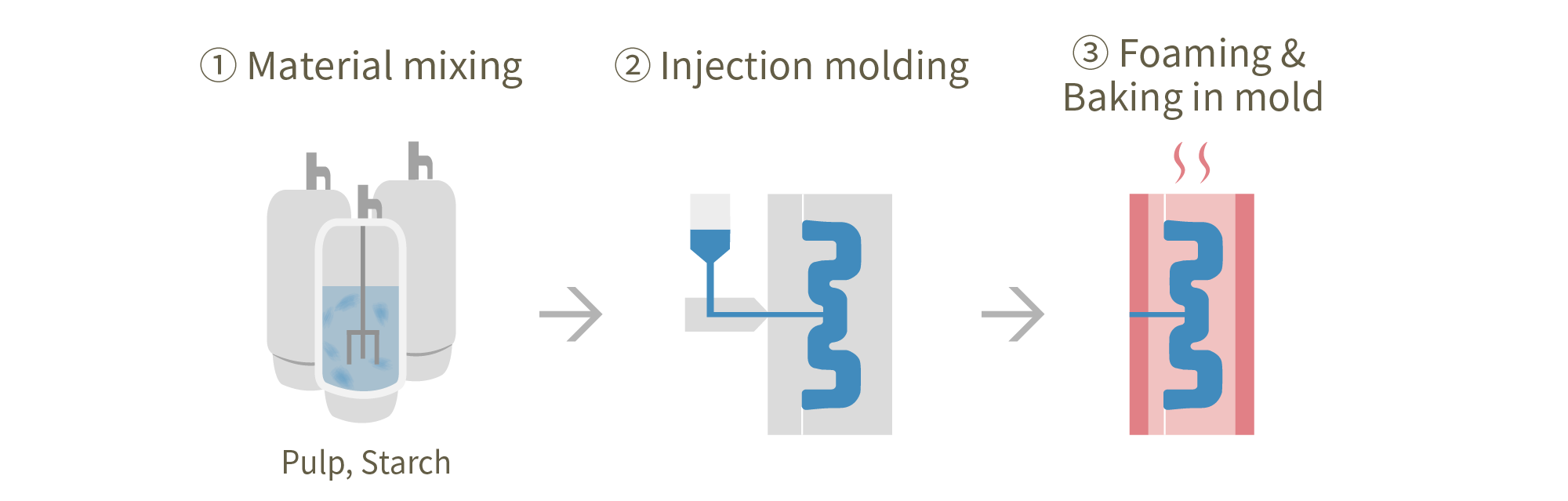
PaperFoam® is characterized by its high cushioning ability to protect products from impacts. Also, it has a high degree of shape freedom, and can reproduce shapes that fit the product, so it is possible to suppress shaking during transport by fixing the product.
PaperFoam® is a technology that is less likely to generate paper dust (dust) and static electricity. Therefore, even for products like earpieces (the ear part of headphones) that are prone to attracting dust on rubber, you can directly place the product without using a plastic individual packaging bag.
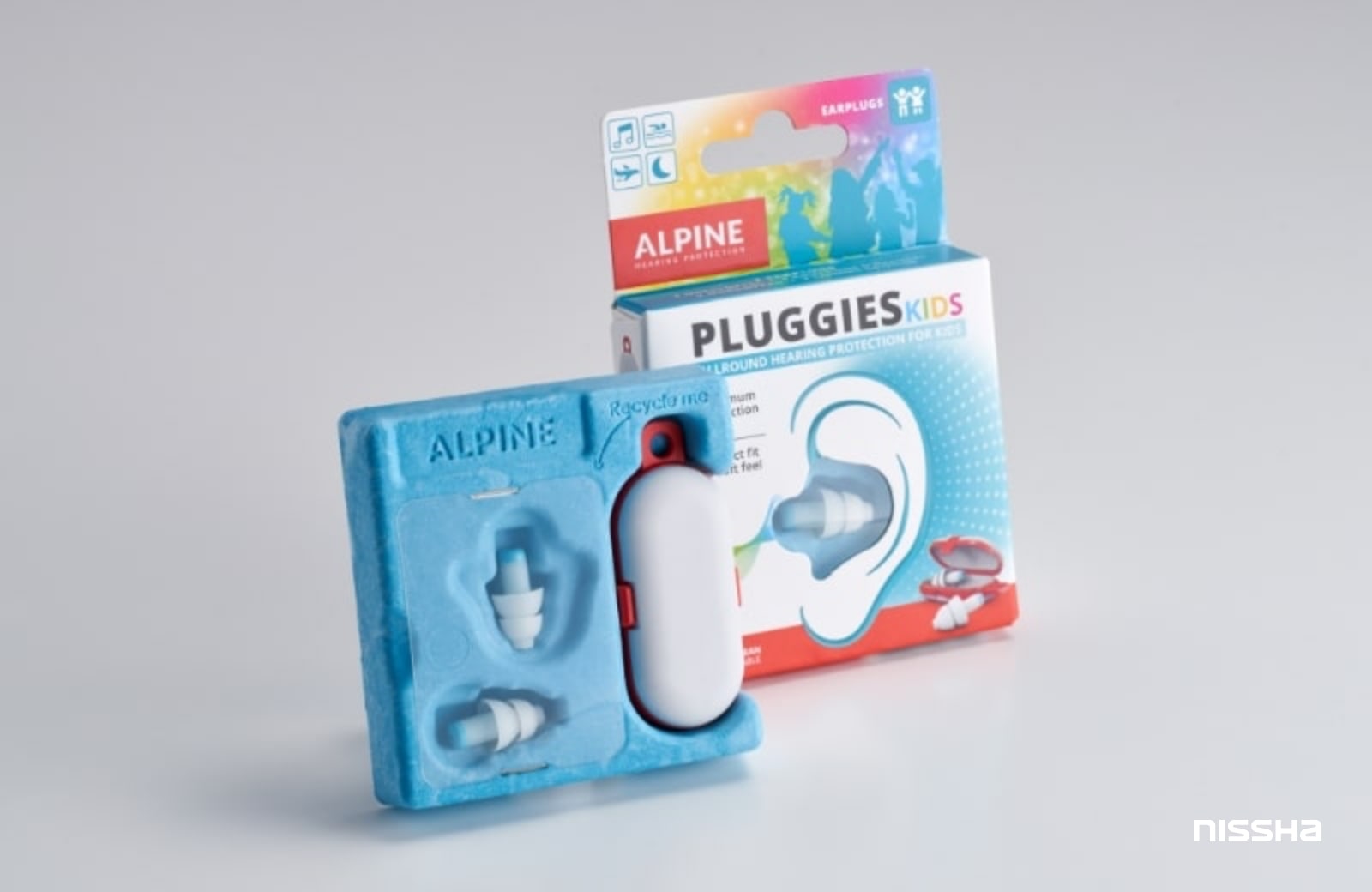

Taking advantage of these features, PaperFoam® is adopted as a tray for a wide range of products, including precision equipment, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. You can find more details here.
Paper-Pressing
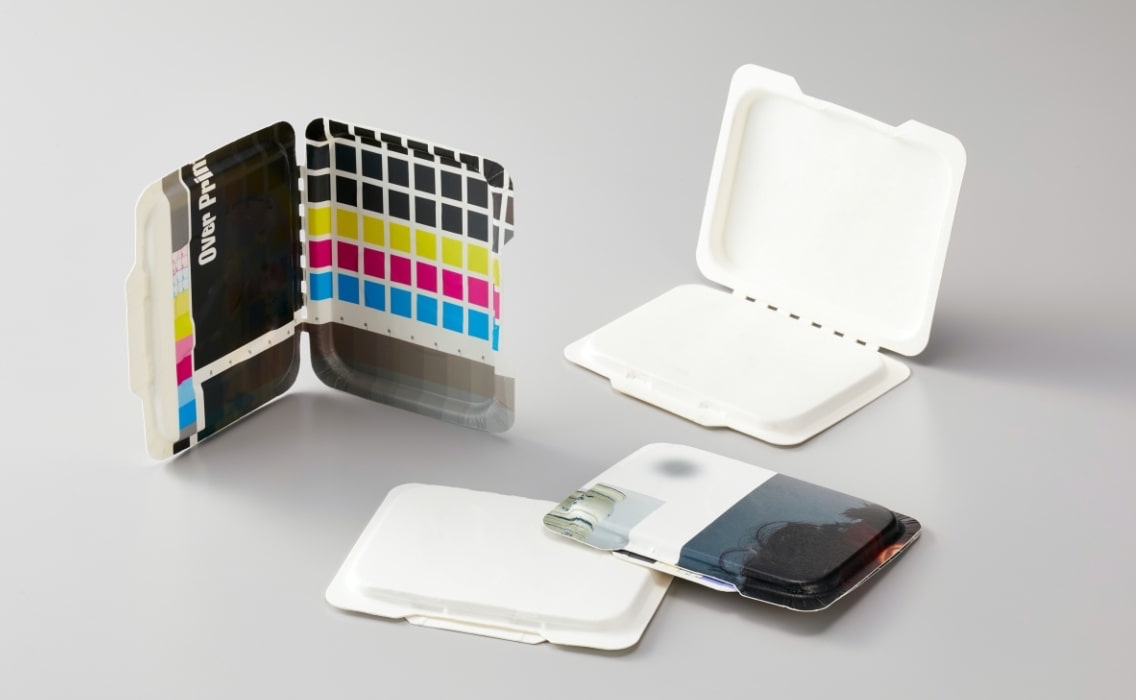

Paper-Pressing is a technology that heats and molds a single sheet of cardboard. Because it uses cardboard as the base material, it can express designs through printing, and it can also form folding lids with hinges and snap fits.
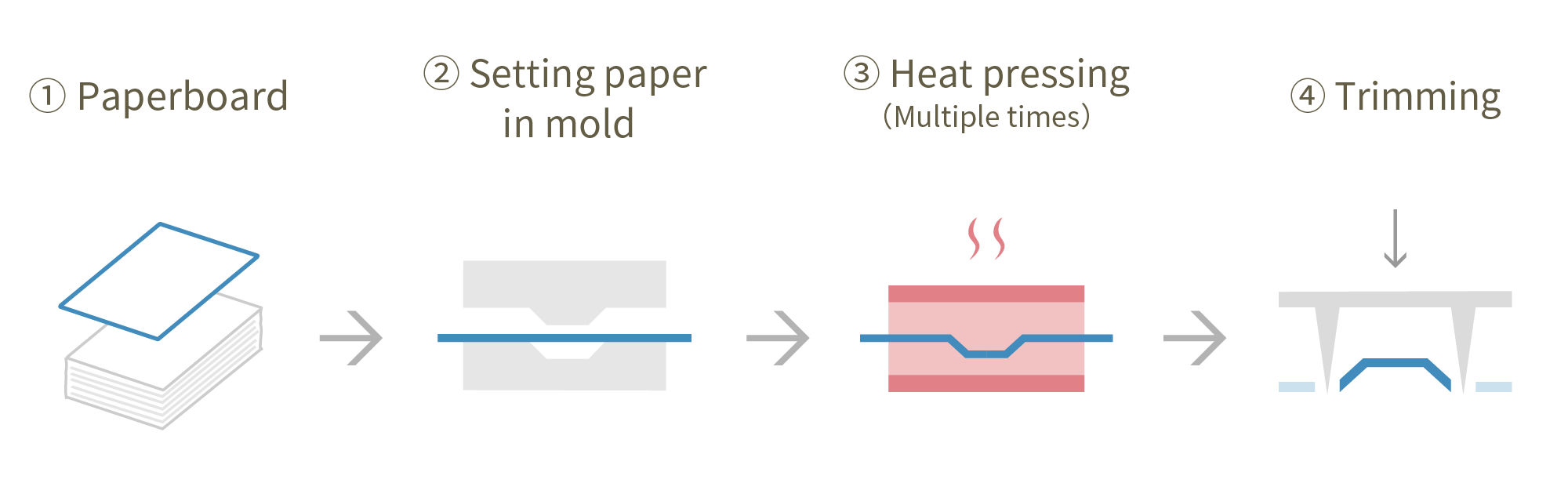
Despite being made from a single sheet of cardboard, Paper-Pressing has the characteristic of having a high-end feel without noticeable paper wrinkles, unlike commonly seen paper plates. Also, oil resistance and water repellency coating are possible.
NISSHA's Initiative “ecosense molding” Aiming to Realize De-plasticization
If you demand the same performance and cost as plastic vacuum-formed trays, de-plasticization may still seem like a high hurdle. However, I hope you understand that efforts to achieve this are being made through various methods.
At NISSHA, under the brand “ecosense molding”, we are working on the development of molding technologies using environmentally friendly materials to contribute to the realization of a sustainable society. We handle a variety of molded products, not just alternatives to vacuum-formed trays, so please check out our product lineup for more details.

